Explain Metabolism of Different Organic Compounds
Primary Metabolites Secondary Metabolites Primary Metabolites These are the chemical compounds produced during the growth and development processes. The four types most important to human structure and function are carbohydrates lipids proteins and nucleic acids.
During metabolism biomolecules present in the food get utilized to extract the energy from the cell.

. Autotrophic prokaryotes use carbon dioxide as their source of carbon. Different metabolic processes break down organic molecules to release the energy for an organism to grow and survive. They are found throughout the world in soils and seas commercial products and every cell of the human body.
Or anabolic the building up synthesis of compounds such as proteins carbohydrates lipids and nucleic acids. Glucose is oxidized with the help of oxygen for the purpose of producing ATP adenosine triphosphate during the process of Cellular Respiration. This processes are necessary for the maintenance of normal vital activity.
-All chemical reactions and physical of the cell. Before exploring these compounds you need to first understand the chemistry of carbon. The molecules in gasoline octane the chemical formula shown contain chemical energy.
Define the term metabolism Metabolism reactions in which organic compounds are from BCH 451 at North Carolina State University. Many are able to use photosynthesis to accomplish this. Of codeine into morphine by CYP2D6.
Phototrophic prokaryotes get their energy from light. The pathway takes in one or more starting molecules and through a series of intermediates converts them into products. In its metabolism of food and respiration an animal consumes glucose C 6 H 12 O 6 which combines with oxygen O 2 to produce carbon dioxide CO 2 water H 2 O and energy which is given off as heat.
Proteins are the main structural blocks of human muscles. Usually catabolism releases energy and anabolism consumes energy. The primary metabolites are formed in the growth phase.
Anabolism This process is mainly involved in building up or synthesizing compounds from simpler subst. A metabolic pathway is a series of chemical reactions that takes a starting molecule and modifies it step-by-step through a series of metabolic intermediates eventually yielding a final product. Anabolism Catabolism This process is mainly involved in breaking down larger organic molecules into smallermolecules.
They are also involved in the primary metabolic processes of respiration and photosynthesis. Tap card to see definition. The process by which plants and other photoautotrophs generate carbohydrates and oxygen from carbon dioxide water and light energy in chloroplasts.
As a result of the need to produce high energy phosphate-containing organic compounds generally in the form of Coenzyme A -esters fermentative organisms use NADH and other cofactors to produce many different reduced metabolic by-products often including hydrogen gas. For the proper functioning of the life of cells the ATP molecules are being used by the animal cells as they act as the main source of energy for metabolism. Phototrophs are organisms that use light as their source of energy to produce ATP and carry.
Plant metabolism of organic compounds shares many processes with mammalian liver function including 1 the capability to detoxify contaminants 2 the specific enzymatic pathways and 3 removal of the compounds from the susceptible organelles. -Forms large molecules from smaller ones. This metabolic process releases energy.
There are two types of metabolic process. Metabolic pathways can be broadly. This energy is transformed into kinetic energy that allows a car to race on a racetrack.
The animal has no need for the carbon dioxide and releases it. The involved chemical modifications incidentally decrease or increase a drugs pharmacological activity andor half-life the most extreme example being the metabolic activation of inactive prodrugs into active drugs eg. Under some circumstances microbial metabolism can consume dissolved oxygen faster than atmospheric oxygen can dissolve into the water or the autotrophic community algae cyanobacteria and macrophytes can produce.
Prokaryotes on the other hand can metabolize a wide range of organic as well as inorganic matter from complex organic molecules like cellulose to inorganic molecules and ions such as atmospheric nitrogen n 2 molecular hydrogen h 2 sulfide s 2 manganese ii ions mn 2 ferrous iron fe 2 and ferric iron fe 3 to name a. The functional group can be defined as an atom or a group of atoms that are joined together in a specific manner which is responsible for the characteristic chemical properties of organic compounds. Catabolism breaking of bonds involves the breaking of biomolecules while anabolism making of bonds is the building of new compounds required by the cells.
-Breaks large molecules to smaller. Heterotrophic metabolism is the biologic oxidation of organic compounds such as glucose to yield ATP and simpler organic or inorganic compounds which are needed by the bacterial cell for biosynthetic or assimilatory reactions. Example of Metabolic Pathways.
The primary objective of drug metabolism is to facilitate a drugs excretion by increasing its water solubility hydrophilicity. All such organic compounds take part in different metabolic pathways for instance in glycolysis Crebs cyclecell respiration. This microbial metabolism creates an oxygen demand proportional to the amount of organic compounds useful as food.
Heterotrophic prokaryotes get organic compounds from other organisms to obtain carbon. Examples in this case are the hydroxyl group -OH aldehyde group -CHO and carboxylic acid group -COOH. The similarities extend to the very structure of the enzymes involved.
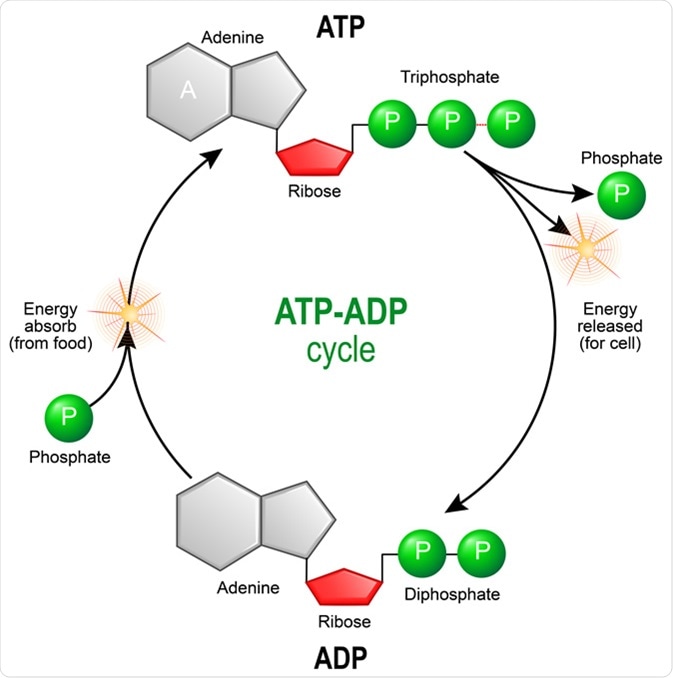
In addition conversion and. Metabolic reactions may be categorized as catabolic the breaking down of compounds for example of glucose to pyruvate by cellular respiration. An important enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of adenosine diphosphate into adenosine triphosphate.
Plant metabolites are of two types. In the example of sugar metabolism the first metabolic pathway synthesized sugar from smaller molecules and the other pathway broke sugar down into smaller molecules. A metabolic pathway is a series of connected chemical reactions that feed one another.
The food which we eat happens to be useless until and unless it undergoes metabolic changes.

Cell Metabolism Learn Science At Scitable

Metabolism Of L Tryptophan Into Serotonin And Melatonin Left And Niacin Right Transfor Organic Chemistry Books Organic Chemistry Study Chemistry Education


No comments for "Explain Metabolism of Different Organic Compounds"
Post a Comment